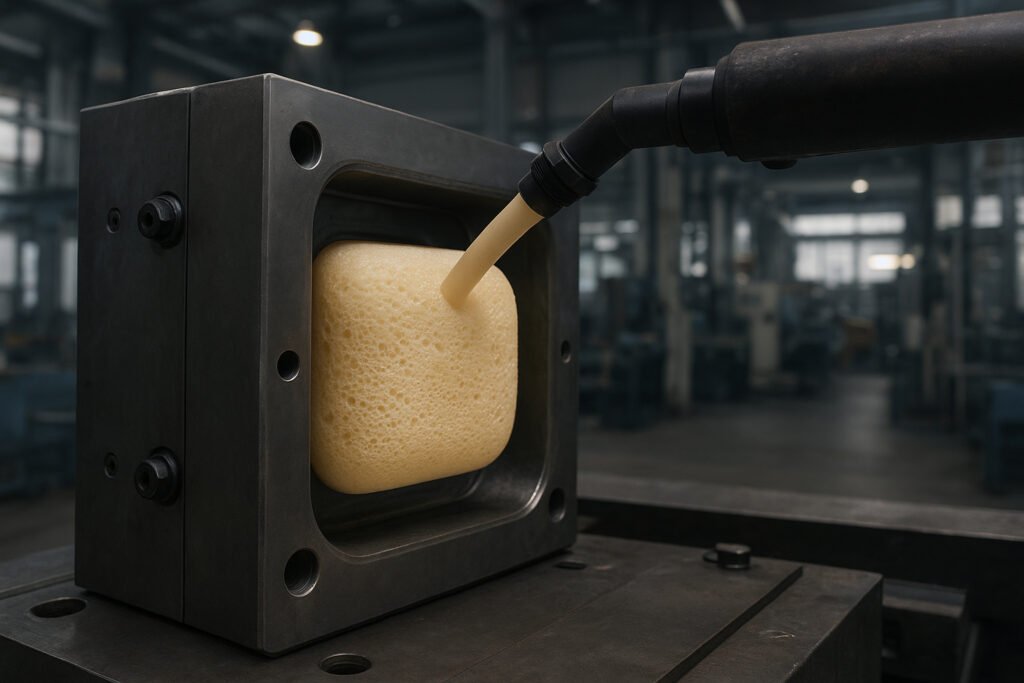
I. Process Overview
Foaming Molding is a processing technology that introduces gas into plastics through physical or chemical methods to form a uniform microporous structure. This process is widely applied in fields such as automobiles, home appliances, packaging, sports equipment and building materials. Foamed products have advantages such as lightweight, heat insulation, buffering and noise reduction, and they are an important development direction for the green and functional development of polymer materials at present.
Ii. Process Flow
Raw material preparation: Mix the resin with the foaming agent, and add additives if necessary to improve dispersion.
Melt mixing: Heat and plasticize in the screw to evenly disperse the foaming agent in the melt.
Injection/mold filling: The melt is injected into the mold under high temperature and high pressure, and the foaming agent begins to decompose or dissolve in gas.
Foaming and molding: By reducing pressure and controlling temperature, gas is released to form a uniform cell structure.
Cooling and shaping: Mold cooling to maintain the shape and cell stability of the product.
Demolding and post-treatment: After the products are removed, they can be cut, trimmed or undergo surface treatment.
Iii. Common Defects and Improvement Measures
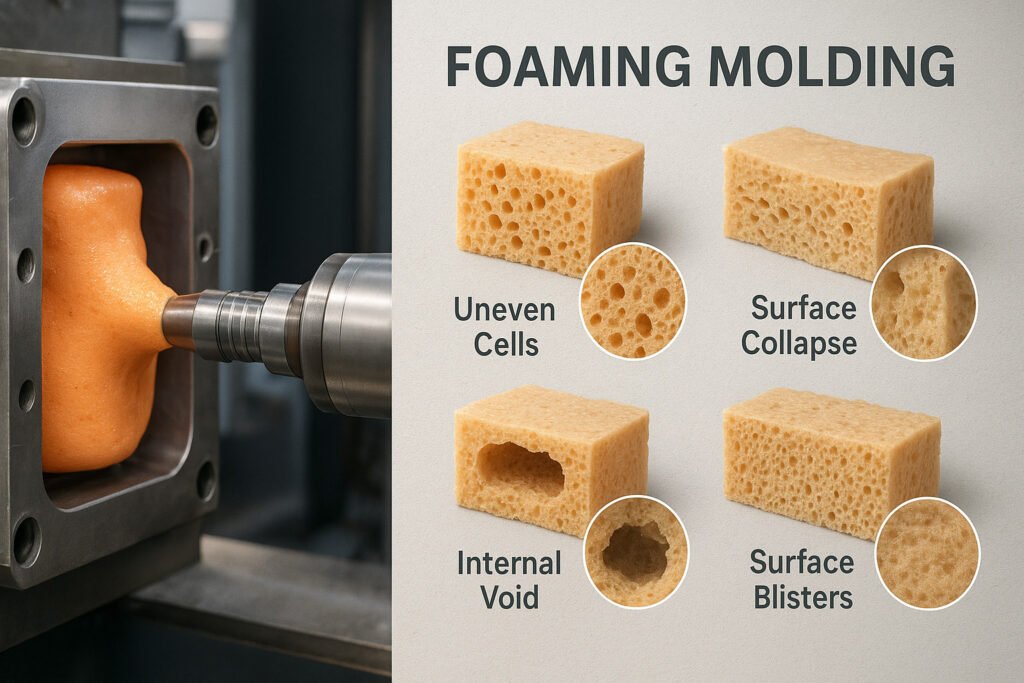
1. Uneven Cell Size/Variation
Phenomenon: The cell distribution of the product is uneven, with some areas being dense and others collapsing. The overall structure is unstable.
Reason: Uneven dispersion of the foaming agent; Fluctuations in melt temperature and pressure; The mold is not cooled evenly.
Improvement measures:
・Increase the back pressure of the screw to 8-12 MPa to promote the uniform mixing of the foaming agent.
・Control the melt temperature within the range of 180 to 220℃ to reduce thermal fluctuations.
・The water temperature for mold cooling should be controlled within ±2℃ to ensure uniform cooling.
Our advantages: We can provide highly compatible resins and stable molecular weight systems to help customers achieve a more uniform cell structure.
2. Surface Collapse/Exposed Cells
Phenomenon: The surface of the product is concave or has exposed pores, which affects its appearance and strength.
Reason: The gas escapes too quickly; Insufficient exhaust from the mold; The cooling speed is too fast.
Improvement measures:
・The depth of the mold exhaust groove should be controlled within 0.02 to 0.04 mm.
・The depressurization time is extended to 1.5-3.0 seconds to avoid sudden pressure loss.
・The surface cooling rate should be controlled at 1-2 ℃/s to prevent collapse.
Our advantages: We have experience in mold optimization and process parameter guidance, and can provide customers with integrated solutions.
3. Internal Voids
Phenomenon: Large holes appear in the cross-section of the product or the center is not filled, reducing the mechanical strength.
Reason: The proportion of foaming agent is too high; Insufficient injection volume; The holding pressure time is insufficient.
Improvement measures:
・The addition amount of foaming agent should be controlled at 0.5-1.5 wt%.
・The injection volume should be maintained at 98-102% of the mold cavity volume.
・The pressure-holding time is extended to 5 to 12 seconds to ensure uniform gas diffusion.
Our advantages: We can recommend highly adaptable foaming agent formulas and provide online process monitoring solutions.
4. Burning and Decomposition
Phenomenon: Local areas show signs of charred yellow or black carbonization, affecting appearance and performance.
Reason: Local melt overheating; The mold temperature is uneven. The foaming agent decomposes too quickly.
Improvement measures:
・Reduce the mold temperature to 60-90℃;
・The upper limit of the melt temperature is controlled at ≤230℃.
・Select a foaming agent with a decomposition temperature of ≥240℃ to ensure stability.
Our advantages: We offer a more stable raw material system and can customize high-temperature resistant process solutions for customers.
5. Surface Bubbles/Silver Streaks
Phenomenon: Blisters, silver-white stripes or fine cracks appear on the surface of the product.
Reason: Gas is released too early; The viscosity of the resin is too low. The surface temperature of the mold is too high.
Improvement measures:
・Control the surface temperature of the mold between 40 and 60 degrees Celsius.
・The melt viscosity is controlled within the range of 200 to 400 Pa·s.
・The injection speed should be controlled at 40-70 mm/s to avoid excessive shearing.
Our advantages: We can supply specialized resins suitable for high-gloss products and provide support for optimizing molding conditions.
6. Unstable Foaming Density
Phenomenon: The density of different parts of the product varies greatly, resulting in inconsistent strength and weight.
Reason: Unstable activity of the foaming agent; Insufficient drying of raw materials; The temperature control or pressure accuracy is insufficient.
Improvement measures:
・The moisture content of raw materials is controlled at ≤0.02%.
・The accuracy of the mold temperature control system is maintained at ±1℃.
・The online weighing accuracy shall not be less than ±0.5%.
Our advantages: We offer low moisture content packaging and a stable supply chain to ensure consistency in our customers' production.
7. Incomplete Foaming
Phenomenon: The product weight is relatively large, the number of cells is small, and the foaming structure is not obvious.
Reason: Insufficient activation of the foaming agent; The melt temperature/pressure is insufficient; The resin gas has poor solubility.
Improvement measures:
・The mold temperature is maintained at 80-110℃.
・The foaming temperature of the foaming agent should be controlled at ≥200℃.
・Maintain the cavity pressure of 8 to 10 MPa to ensure the dissolution of the gas.
Our advantages: We can recommend targeted foaming agents and modified materials to help customers achieve the ideal foaming ratio.
8. Cracks/Surface Roughness
Phenomenon: The surface of the product is rough or has micro-cracks, which affects its strength and appearance.
Reason: Too fast cooling; The cells are too large or unevenly distributed; The melt strength is insufficient.
Improvement measures:
・The cooling rate should be controlled at ≤3 ℃/s.
・The foaming ratio should be controlled at 2 to 4 times to avoid being too high.
・Select high-toughness resin with a melt strength of ≥ 0.25N.
Our advantages: We can provide tough-enhanced materials, significantly improving the appearance and structural integrity of products.
Iv. Application Fields
Industria automotriz: lightweight interior parts, cushioning pads, noise reduction materials.
Household appliances and packaging: Insulation layer, shockproof packaging.
Architecture and Engineering: Insulation boards, shock-absorbing materials.
Sports equipment: Shoe soles, protective gear, buoyancy products.
V. Our Supply Advantages
As a professional supplier of plastic raw materials, we not only provide high-quality foaming molding grade resins, but also help customers solve process problems
・Stable quality: Strictly control the melt index and foaming agent compatibility to ensure batch consistency.
・Low moisture content guarantee: Vacuum-packed and inspected before leaving the factory to reduce bubble and cavity defects.
・Multi-category supply: One-stop service for PE, PÁGINAS, EVA, TPU and various physical/chemical foaming agents.
・International service experience: Covering multiple markets, providing logistics and after-sales support.
・Technical support: Based on the customer's process, we recommend the optimal formula and material solutions to enhance production capacity and yield.
Vi. Summary
Foaming Molding is a key technology for lightweighting and functionalizing plastic products, but defect control is crucial for quality and cost. By selecting stable foaming-grade raw materials and optimizing process parameters and mold design, product performance and market competitiveness can be significantly improved. As a trusted plastic raw material supplier, we are committed to providing high-quality resins and professional technical support to global buyers, jointly promoting the development of foam molding applications. Analyze whether this article is relevant to the industry and whether it is professional.


