I. From "Cheap Materials" to "High-performance Materials" : The Comeback of Plastic
In the public's impression, "plastic" implies being thin, fragile and not durable.
However, in modern manufacturing, this concept has long been outdated.
Today's Engineering Plastics can rival or even surpass some metals in terms of strength, toughness and heat resistance, and are widely used in high-demand fields such as automobiles, aviation, electronics and medical care.
The key behind this is not "magic", but science.
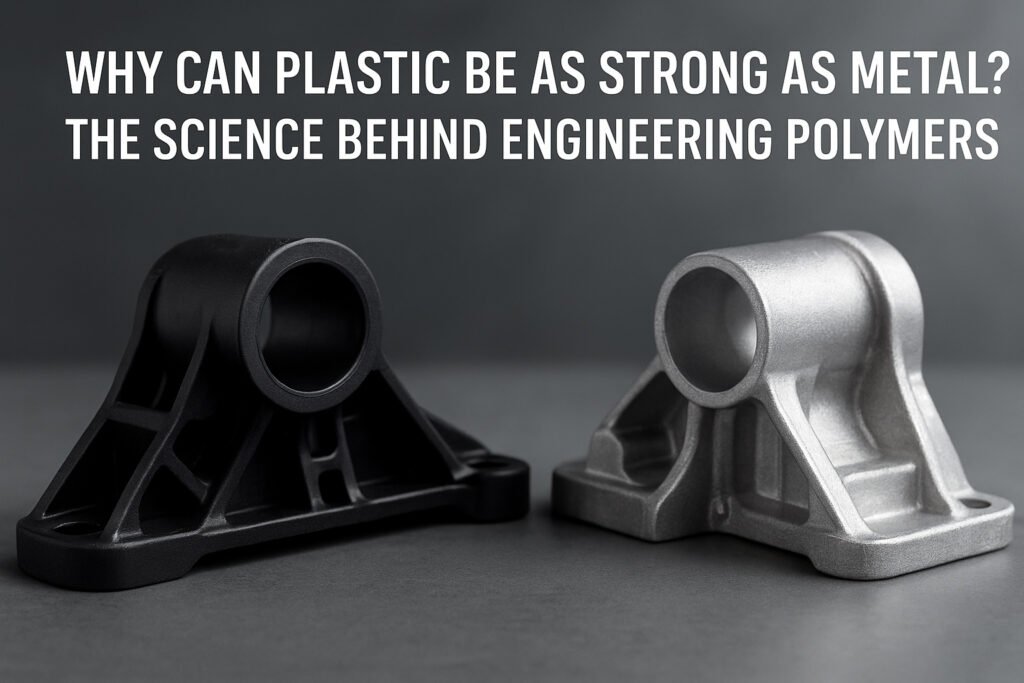
Ii. Scientific Basis: Why is Plastic So Strong?
1. The polymer chain structure endows a strong and tough skeleton
・The strength of engineering plastics comes from the arrangement and bonding force of polymer chains.
・These molecular chains are like "molecular reinforcing bars", interconnected through forces such as covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds, making the material less prone to breakage when subjected to external forces.
・For instance, the hydrogen bonds between PA (nylon) molecules form crystalline regions, significantly enhancing its tensile strength and wear resistance.
2. Glass fiber/carbon fiber filling technology enhances rigidity
・Modified plastics with added glass fiber (GF) or carbon fiber (CF) can increase their strength by 30% to 200%.
・For instance, the tensile strength of GF30% reinforced PA66 can reach 170 MPa, approaching the level of aluminum alloys.
・This is precisely the fundamental reason why engineering plastics are rapidly replacing metals in fields such as automotive structural components and electronic casings.
3. Special plastics: high-temperature resistant, impact-resistant, fatigue-resistant
・High-performance polymers like PEEK, PPS and PBT not only have high strength but also can work for a long time at temperatures above 200°C.
・Their molecular main chains are mostly aromatic ring structures, which possess outstanding thermal stability and fatigue resistance.
・This makes them the preferred materials for aerospace, medical devices and electrical connectors.
Iii. Typical Materials and Cases
| Material | Features | Typical Applications |
| PC (Polycarbonate) | High transparency, impact resistance | Bulletproof glass, helmets, optical lenses |
| PA (Nylon) | High strength, wear and oil resistance | Automotive gears, mechanical bearings |
| PBT | Good electrical properties and dimensional stability | Electronic connectors, appliance housings |
| PEEK | Extremely high strength and heat resistance | Aerospace components, medical implants |
The common features of these materials are: lightweight, high strength and resistance to environmental stress.
They elevated the concept of "plastic" from a daily necessity to a "structural material".
Iv. Comparison with Metals: Advantages and Limitations of Plastics
| Comparison Dimension | Engineering Plastics | Metal |
| Weight | Light (about 1/6 the density of metal) | Heavy |
| Molding Cost | Low, suitable for injection molding | High, requires machining |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, non-rusting | Moderate, requires protection |
| Thermal Conductivity | Weak | Strong |
| Recyclability | Improving (mechanical/chemical recycling) | Mature |
The conclusion is clear: Plastic is not a substitute for metal, but a new solution.
It provides a sustainable path for lightweight and low-carbon manufacturing.
V. Future Trends: Making Plastic "More Like Metal"
1. Carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) is on the rise
CFRP combines the strength of carbon fiber with the lightweight characteristics of plastic and is widely used in electric vehicle structural components and the aerospace field.
2. The trend of metal substitution is obvious
In new energy vehicles, robots and 5G devices, engineering plastics such as PA, PBT and PEEK are gradually replacing metal components like aluminum and magnesium.
3. Intelligent modification and circular innovation
Nanofillers, self-healing polymers and recyclable engineering plastics are becoming research hotspots.
This makes plastic not only "strong", but also "smart" and "sustainable".
Vi. Conclusion: Plastic, the "New Metal" of Modern Industry
Plastic is no longer merely a "cheap alternative".
It is becoming the most promising structural material and innovative carrier in the modern industrial system.
At Juyuan, we are committed to providing high-performance engineering plastic raw material solutions for global customers, including
・Glass fiber reinforced PA, PC, PBT;
・High-temperature resistant PEEK, PPS;
・Recycled engineering plastics that meet environmental protection requirements.
💡 Plastics are not weak, but strong in the future.

